THE UNIVERSITY
OF THE STATE OF NEW YORK
Regents
of The University
Robert M. Bennett, Chancellor, B.A., M.S. ....................................................................... Tonawanda
Adelaide L. Sanford, Vice Chancellor, B.A.,
M.A., P.D. ............................................... Hollis
Diane O’Neill McGivern, B.S.N., M.A., Ph.D. .............................................................. Staten Island
Saul B. Cohen, B.A., M.A., Ph.D............................................................................................ New Rochelle
James C. Dawson, A.A., B.A., M.S., Ph.D. .......................................................................... Peru
Robert M. Johnson, B.S., J.D. ............................................................................................... Huntington
Anthony S. Bottar, B.A., J.D. ............................................................................................. North Syracuse
Merryl H. Tisch, B.A., M.A. ................................................................................................... New York
Geraldine D. Chapey, B.A., M.A., Ed.D........................................................................... Belle Harbor
Arnold B. Gardner, B.A., LL.B........................................................................................... Buffalo
Harry Phillips,
3rd, B.A., M.S.F.S. ...................................................................................... Hartsdale
Joseph E. Bowman, Jr., B.A., M.L.S., M.A.,
M.Ed., Ed.D................................................ Albany
Lorraine A. CortÉs-VÁzquez, B.A., M.P.A.................................................................. Bronx
Judith O. Rubin, A.B. ................................................................................................................ New York
James R. Tallon, jr., B.A., M.A. .......................................................................................... Binghamton
Milton L. Cofield, B.S., M.B.A.,
Ph.D. ............................................................................... Rochester
President of The University and Commissioner of
Education
Richard P. Mills
Chief Operating Officer
Richard H. Cate
Deputy Commissioner for Elementary, Middle,
Secondary and Continuing Education
James A. Kadamus
Coordinator, School Operations and Management
Services
Charles Szuberla
Coordinator, Information and Reporting Services
Martha P. Musser
The State Education Department does not discriminate on
the basis of age, color, religion, creed, disability, marital status, veteran
status, national origin, race, gender, genetic predisposition or carrier
status, or sexual orientation in its educational programs, services and
activities. Portions of this
publication can be made available in a variety of formats, including braille,
large print or audio tape, upon request.
Inquiries concerning this policy of nondiscrimination should be directed
to the Department’s Office for Diversity, Ethics, and Access, Room 530,
Education Building, Albany, NY 12234. Requests
for additional copies of this publication may be made by contacting the
Publications Sales Desk, Room 309, Education Building, Albany, NY 12234.
Please
address all correspondence about this report that is not related to data corrections
to:
School Report Card Coordinator
Information and Reporting
Services Team
New York State Education
Department
Room 863 EBA
89 Washington Avenue
Albany, NY 12234
E-mail: RPTCARD@mail.nysed.gov
The New York State Report Card is an important part of the Board of
Regents effort to raise learning standards for all students. It provides
information to the public on student performance and other measures of
performance. Knowledge gained from the report card on the State’s strengths and
weaknesses can be used to improve instruction and services to students.
The
New York State Report Card consists
of three parts: the Overview of
Performance in English Language Arts, Mathematics, and Science and Analysis of Student Subgroup
Performance, the Comprehensive
Information Report, and the
Accountability Report. The Overview
and Analysis presents performance data on measures required by the
federal No Child Left Behind Act: English, mathematics, science, and graduation
rate. Performance data on other State assessments can be found in the Comprehensive Information Report. The Accountability Report provides
information as to whether a district/school is making adequate progress toward
enabling all students to achieve proficiency in English and mathematics.
State assessments are designed to
help ensure that all students reach high learning standards. They show whether
students are getting the foundation knowledge they need to succeed at the
elementary, middle, and commencement levels and beyond. The State requires that
students who are not making appropriate progress toward the standards receive
academic intervention services.
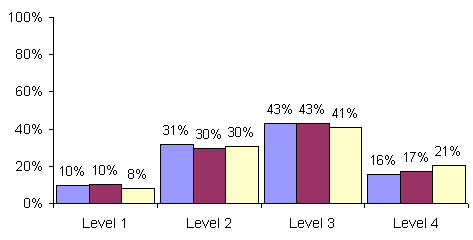
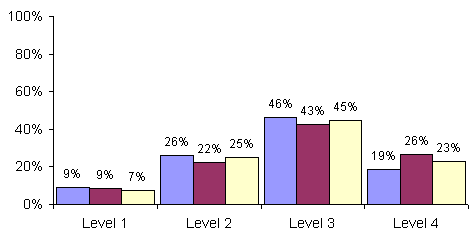
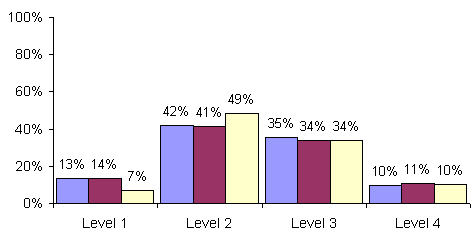
In the Overview, performance on the elementary- and middle-level
assessments in English language arts and mathematics and on the middle-level
science test is reported in terms of mean scores and the percentage of students
scoring at each of the four levels. These levels indicate performance on the
standards from seriously deficient to advanced proficiency. Performance on the
elementary-level science test is reported in terms of mean scores and the
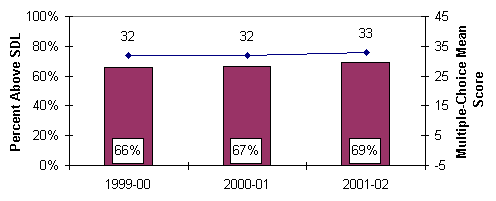
percentage of students making appropriate progress. Regents examination scores
are reported in four score ranges. Scores of 65 to 100 are passing; scores of
55 to 64 earn credit toward a local diploma (with the approval of the local
board of education). Though each elementary- and middle-level assessment is
administered to students in a specific grade, secondary-level assessments are
taken by students when they complete the coursework for the core curriculum.
Therefore, the performance of students at the secondary level is measured for a
student cohort rather than a group of students at a particular grade level.
Students are grouped in cohorts according to the year in which they first
entered grade 9.
The assessment data in the Overview and Analysis are for all tested
students in the State, including general-education students and students with
disabilities. In the Analysis,
performance is disaggregated by race/ethnicity, disability status, gender, LEP
status, income level, and migrant status.
Explanations of terms referred to or
symbols used in this part of the report card may be found in the glossary on
the last page. Further information on the report card may be found in the
guide, Understanding Your School Report
Card 2003, available at your district or on the Information and Reporting
Services Web site at www.emsc.nysed.gov/irts.
Overview of Statewide Performance
in
English Language Arts, Mathematics, and Science
State Profile
|
Organization
2001–02
|
School Statewide Staff (both full-
and part-time)
|
|
Grade Range
|
Student Enrollment
|
Count of Teachers
|
Count of Other Professionals
|
|
K-12
|
2,828,318
|
217,739
|
40,823
|
|
2000–01
NYS Public Schools Total Expenditure per Pupil
|
$11,871
|
|
Student
Demographics
|
1999–2000
|
2000–2001
|
2001–2002
|
|
Count*
|
Percent
|
Count*
|
Percent
|
Count*
|
Percent
|
|
Limited English
Proficient
|
230,625
|
8.1%
|
201,319
|
7.0%
|
193,605
|
6.8%
|
|
Eligible for Free
Lunch
|
1,064,388
|
38.2%
|
1,061,386
|
38.1%
|
1,054,668
|
37.7%
|
*Counts of limited English proficient students and students
eligible for free lunch in 1999–2000 do not
include charter schools. Counts in 2000–2001 and 2001–2002 include charter
schools.
2001–02
Percentage of Core Classes Taught by Highly Qualified Teachers*
|
Number of
Core Classes
|
Percent
Taught by Highly Qualified Teachers
|
|
441,140
|
87%
|
2001–02
Percentage of Teachers with No Valid Teaching Certificate*
|
Number of
Teachers
|
Percent No
Valid Teaching Certificate
|
|
212,441
|
8%
|
*This
count includes teachers with temporary licenses who do not have a valid
permanent or provisional teaching certificate.
Glossary
Cohort Data: A student cohort is all students, regardless of grade
status, who were enrolled in school on BEDS day two years after the year in
which they entered grade 9, or, in the case of ungraded students with
disabilities, the year in which they reached their seventeenth birthday. (For
example, the 1998 cohort consists of all students who first entered grade 9 in
the fall of 1998 who were enrolled on October 4, 2000). Certain severely
disabled students, new immigrants, and students who transfer to programs
leading to a high school diploma or high school equivalency diploma are not
included in the school cohort. Cohort is defined in Section 100.2 (p) (8) (iii)
of the Commissioner’s Regulations. Data
for the 1997 cohort are based on the Special Regents Examination Report for the
1997 Cohort. Data for the 1998 cohort are based on the 2002 STEP file submitted
by each district.
Component Retests: Component retests were offered in Regents English and
Mathematics A to graduating seniors who were at risk of not meeting the State
learning Standards. Component retesting is the process by which a student who
has failed a Regents examination in English or Mathematics A twice is retested
only on the areas of the learning standards in which the student has been
proven deficient. Component retesting eliminates the need for the student to
retake the full Regents examination multiple times. Students who earn credit
through component retesting are counted as if they scored in the 55–64 range or
in the 65–84 range, as determined by the results of the component retest.
Counts of Students Tested: “Counts of Students Tested” includes only students who
completed sufficient test questions to receive a score.
Limited English Proficient (LEP)
Students: Schools teach
English to students for whom English is a second language so they can
participate effectively in the academic program. Students are considered LEP
if, by reason of foreign birth or ancestry, they speak a language other than
English and (1) either understand and speak little or no English or (2) score
at or below the 40th percentile on an English language assessment
instrument. LEP students without sufficient proficiency in English were not
required to take the grade 4 or grade 8 English language arts test. Their
reported progress in learning English was measured using standardized tests.
New York State Alternate
Assessment (NYSAA): The district
Committee on Special Education designates severely disabled students who meet
criteria established in Commissioner’s Regulations to take the New York State
Alternate Assessment (NYSAA).
Student
Confidentiality/Suppressed Data (# and s):
To ensure student confidentiality, the Department does not publish data for groups with fewer than five students or
data that would allow readers to easily determine the performance of a group
with fewer than five students. In the Overview,
the pound character (#) appears when fewer than five students in a group
were tested. In the Analysis, when
fewer than five students in a group (e.g., Hispanic) were tested, percentages
of tested students scoring at various levels were suppressed for that group and
the next smallest group. Suppressed
data are indicated with an (s). However, the performance of tested students
in these groups is aggregated and shown in the Small Group Total row.
Validity and Reliability of Small
Group Data: It is important that
programmatic decisions are based on valid and reliable data. Data for fewer
than 40 students in a group are neither valid nor reliable. If a school does not have 40 students in a
grade or a subgroup in a given year, the school should evaluate results for
students in this group over a period of years to make programmatic decisions.